Bowhead whale
| Bowhead whale[1] Temporal range: Early Pleistocene[2] to recent
| |
|---|---|

| |

| |
| Size compared to an average human | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Artiodactyla |
| Infraorder: | Cetacea |
| Family: | Balaenidae |
| Genus: | Balaena |
| Species: | B. mysticetus
|
| Binomial name | |
| Balaena mysticetus | |

| |
| Bowhead whale range | |
The bowhead whale (Balaena mysticetus) is a species of baleen whale belonging to the family Balaenidae and is the only living representative of the genus Balaena. It is the only baleen whale endemic to the Arctic and subarctic waters, and is named after its characteristic massive triangular skull, which it uses to break through Arctic ice. Other common names of the species included the Greenland right whale, Arctic whale, steeple-top, and polar whale.[5]
Bowheads have the largest mouth of any animal[6] representing almost one-third of the length of the body, the longest baleen plates with a maximum length of 4 m (13 ft),[7] and may be the longest-lived mammals, with the ability to reach an age of more than 200 years.[8]
The bowhead was an early whaling target. Their population was severely reduced before a 1966 moratorium was passed to protect the species. Of the five stocks of bowhead populations, three are listed as "endangered", one as "vulnerable", and one as "lower risk, conservation dependent" according to the IUCN Red List. The global population is assessed as of least concern.[3][9]
Taxonomy
[edit]Carl Linnaeus named this species in the tenth edition of his Systema Naturae (1758).[10] It was seemingly identical to its relatives in the North Atlantic, North Pacific, and Southern Oceans, and as such they were all thought to be a single species, collectively known as the "right whale", and given the binomial name Balaena mysticetus.
Today, the bowhead whale occupies a monotypic genus, separate from the right whales, as proposed by the work of John Edward Gray in 1821.[11] For the next 180 years, the family Balaenidae was the subject of great taxonometric debate. Authorities have repeatedly recategorized the three populations of right whale plus the bowhead whale, as one, two, three or four species, either in a single genus or in two separate genera. Eventually, it was recognized that bowheads and right whales were different, but there was still no strong consensus as to whether they shared a single genus or two. As recently as 1998, Dale Rice listed just two species – B. glacialis (the right whales) and B. mysticetus (the bowheads) – in his comprehensive and otherwise authoritative classification.[12]
Studies in the 2000s finally provided clear evidence that the three living right whale species comprise a phylogenetic lineage, distinct from the bowhead, and that the bowhead and the right whales are rightly classified into two separate genera.[13] The right whales were thus confirmed to be in a separate genus, Eubalaena. The relationship is shown in the cladogram below:
| Family Balaenidae | |||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||
| The bowhead whale, genus Balaena, in the family Balaenidae (extant taxa only)[14] |
The earlier fossil record shows no related cetacean after Morenocetus, found in a South American deposit dating back 23 million years.
An unknown species of right whale, the so-called "Swedenborg whale", which was proposed by Emanuel Swedenborg in the 18th century, was once thought to be a North Atlantic right whale. Based on later DNA analysis, those fossil bones claimed to be from Swedenborg whales were confirmed to be from bowhead whales.[15]
Description
[edit]

The bowhead whale has a large, robust, dark-coloured body and a white chin. It has a massive triangular skull, which it uses to break through the Arctic ice to breathe. Inuit hunters have reported bowheads surfacing through 60 cm (24 in) of ice.[16] It also possesses a strongly bowed lower jaw and a narrow upper jaw. Its baleen is the longest of that of any whale, at 3 m (9.8 ft), and is used to strain tiny prey from the water. The bowhead whale has paired blowholes at the highest point of the head, which can spout a blow 6.1 m (20 ft) high. The bowhead's blubber is the thickest of any animal's, with a maximum of 43–50 cm (17–20 in).[17] Unlike most cetaceans, the bowhead does not have a dorsal fin—an adaptation for spending much time under sea-surface ice.[18] Like the sperm whale and other cetaceans, the bowhead whale has a vestigial pelvis that is not connected to the spine.
Bowhead whales are comparable in size to the three species of right whales. According to whaling captain William Scoresby Jr., the longest bowhead he measured was 17.7 m (58 ft) long, while the longest measurement he had ever heard of was of a 20.4 m (67 ft) whale caught at Godhavn, Greenland, in early 1813. He also spoke of one, caught near Spitsbergen around 1800, that was allegedly nearly 21.3 m (70 ft) long.[19] In 1850, an American vessel claimed to have caught a 24.54 m (80+1⁄2 ft) individual in the Western Arctic.[20] Whether these lengths were actually measured is questionable. The longest reliably measured were a male of 16.2 m (53 ft) and a female of 18 m (59 ft), both landed in Alaska.[21] On average, female bowheads are larger than males. The adults would have likely measured 19 m (62 ft) in length and 80 t (88 short tons; 79 long tons) in body mass, but larger individuals (like the one claimed in 1850) may weigh up to 100 t (110 short tons; 98 long tons).[22]
Analysis of hundreds of DNA samples from living whales and from baleen used in vessels, toys, and housing material has shown that Arctic bowhead whales have lost a significant portion of their genetic diversity in the past 500 years. Bowheads originally crossed ice-covered inlets and straits to exchange genes between Atlantic and Pacific populations. This conclusion was derived from analyzing maternal lineage using mitochondrial DNA. Whaling and climatic cooling during the Little Ice Age, from the 16th century to the 19th, is supposed to have reduced the whales' summer habitats, which explains the loss of genetic diversity.[23]
A 2013 discovery has clarified the function of the bowhead's large palatal retial organ. The bulbous ridge of highly vascularized tissue, the corpus cavernosum maxillaris, extends along the centre of the hard plate, forming two large lobes at the rostral palate. The tissue is histologically similar to that of the corpus cavernosum of the mammalian penis. This organ is thought to provide a mechanism of cooling for the whale (which is normally protected from the cold Arctic waters by 40 cm (16 in) or more of fat). During physical exertion, the whale must cool itself to prevent hyperthermia (and ultimately brain damage). This organ becomes engorged with blood, and as the whale opens its mouth cold seawater flows over the organ, thus cooling the blood.[24]
Behaviour
[edit]

Swimming
[edit]The bowhead whale is not a social animal, typically travelling alone or in small pods of up to six. It is able to dive and remain submerged under water for up to an hour. The time spent under water in a single dive is usually limited to 9–18 minutes.[16] The bowhead is not thought to be a deep diver, but can reach a depth down to 150 m (500 ft). It is a slow swimmer, normally travelling around 2–5 km/h (0.56–1.39 m/s; 1.2–3.1 mph).[25] When fleeing from danger, it can travel at a speed of 10 km/h (2.8 m/s; 6.2 mph). During periods of feeding, the average swim speed is increased to 1.1–2.5 m/s (4.0–9.0 km/h; 2.5–5.6 mph).[26]
Feeding
[edit]The head of the bowhead whale comprises a third of its body length, creating an enormous feeding apparatus.[26] The bowhead whale is a filter feeder, and feeds by swimming forward with its mouth wide open.[16] It has hundreds of overlapping baleen plates consisting of keratin hanging from each side of the upper jaw. The mouth has a large, upturning lip on the lower jaw that helps to reinforce and hold the baleen plates within the mouth. This also prevents buckling or breakage of the plates from the pressure of the water passing through them as the whale advances. To feed, water is filtered through the fine hairs of keratin of the baleen plates, trapping the prey inside near the tongue where it is then swallowed.[27] The diet consists of mostly zooplankton, which includes krill, copepods, mysids, amphipods, and many other crustaceans.[26][28] About 1.8 t (2 short tons) of food are consumed each day.[27] While foraging, bowheads are solitary or occur in groups of two to 10 or more.[17]
Vocalization
[edit]Bowhead whales are highly vocal[29] and use low frequency (<1000 Hz) sounds to communicate while travelling, feeding, and socialising. Intense calls for communication and navigation are produced especially during migration season. During breeding season, bowheads make long, complex, variable songs for mating calls.[25] Many tens of distinct songs are sung by a population in a single season.[30] From 2010 through to 2014, near Greenland, 184 distinct songs were recorded from a population of around 300 animals.[31]
Reproduction
[edit]Sexual activity occurs between pairs and in boisterous groups of several males and one or two females. Breeding season is observed from March through August; conception is believed to occur primarily in March when song activity is at its highest.[25] Reproduction can begin when a whale is 10 to 15 years old. The gestation period is 13–14 months with females producing a calf once every three to four years.[21] Lactation typically lasts about a year. To survive in the cold water immediately after birth, calves are born with a thick layer of blubber. Within 30 minutes of birth, bowhead calves are able to swim on their own. A newborn calf is typically 4–4.5 m (13–15 ft) long, weighs roughly 1,000 kg (2,200 lb), and grows to 8.2 m (27 ft) within the first year.[21]
Health
[edit]Lifespan
[edit]Bowhead whales are considered to be the longest-living mammals, living for over 200 years.[32] In May 2007, a 15 m (49 ft) specimen caught off the Alaskan coast was discovered with the 89 mm (3.5 in) head of an explosive bomb lance of a model manufactured between 1879 and 1885 lodged in its body, so the whale was probably bomb lanced sometime between those years, and its age at the time of death was estimated at between 115 and 130 years.[33] Spurred by this discovery, scientists measured the ages of other bowhead whales; one specimen was estimated to be 211 years old.[34] Other bowhead whales were estimated to be between 135 and 172 years old. This discovery showed the longevity of the bowhead whale is much greater than originally thought.[35] Researchers at CSIRO, Australia's national science agency, estimated that bowhead whales' maximum natural lifespan is 268 years based on genetic analysis.[36]
Genetic benefits
[edit]A greater number of cells present in an organism was once believed to result in greater chances of mutations that cause age-related diseases and cancer.[37] Although the bowhead whale has thousands of times more cells than other mammals, it has a much higher resistance to cancer and aging. In 2015, scientists from the US and UK were able to successfully map the whale's genome.[38] Through comparative analysis, two alleles that could be responsible for the whale's longevity were identified. These two specific gene mutations linked to the bowhead whale's ability to live longer are the ERCC1 gene and the proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA) gene. ERCC1 is linked to DNA repair and increased cancer resistance. PCNA is also important in DNA repair. These mutations enable bowhead whales to better repair DNA damage, allowing for greater resistance to cancer.[37] The whale's genome may also reveal physiological adaptations such as having low metabolic rates compared to other mammals.[39] Changes in the gene UCP1, a gene involved in thermoregulation, can explain differences in the metabolic rates in cells.
Ecology
[edit]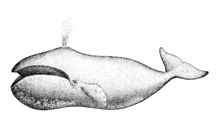
Range and habitat
[edit]The bowhead whale is the only baleen whale to spend its entire life in the Arctic and subarctic waters.[40] The Alaskan population spends the winter months in the southwestern Bering Sea. The group migrates northward in the spring, following openings in the ice, into the Chukchi and Beaufort seas.[41] The whale's range varies depending on climate changes and on the forming/melting of ice.[42]
Historically, bowhead whales' range may have been broader and more southerly than currently thought. Bowheads were abundant around Labrador, Newfoundland (Strait of Belle Isle) and the northern Gulf of St Lawrence until at least the 16th and 17th centuries. It is unclear whether this was due to the colder climate during these periods.[43] The distribution of Balaena spp. during the Pleistocene were far more southerly as fossils have been excavated from Italy and North Carolina, thus could have overlapped between those of Eubalaena based on those locations.[44]
Population
[edit]Generally, five stocks of bowhead whales are recognized: 1) the Western Arctic stock in the Bering, Chukchi, and Beaufort Seas, 2) the Hudson Bay and Foxe Basin stock, 3) the Baffin Bay and Davis Strait stock, 4) the Sea of Okhotsk stock, and 5) the Svalbard-Barents Sea stock. However, recent evidence suggests that the Hudson Bay and Foxe Basin stock and the Baffin Bay and Davis Strait stock should be considered one stock based on genetics and movements of tagged whales.[45]
Western Arctic
[edit]The Western Arctic bowhead population, also known as the Bering-Chukchi-Beaufort population, has recovered since the commercial harvest of this stock ceased in the early 1900s. A 2019 study estimated that the Western Arctic population was 12,505; although it was lower than the 2011 value of 16,820, the surveyors believed there was no significant decline in 2011–2019 due to the unusual conditions of whale migration and observation in 2019.[46] The yearly growth rate of the Western Arctic bowhead population was 3.7% from 1978 to 2011. These data suggest that the Western Arctic bowhead stock may be near its precommercial whaling level.[45] Migration patterns of this population are being affected by climate change.[47]
Alaskan Natives continue to hunt small numbers of bowhead whales for subsistence purposes. The Alaska Eskimo Whaling Commission co-manages the bowhead subsistence harvest with the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. The Alaskan villages that participate in the bowhead subsistence harvest include Barrow, Point Hope, Point Lay, Wainwright, Nuiqsut, Kaktovik, Gambell, Savoonga, Kivalina, Wales, and Little Diomede.[48] The annual subsistence harvest of the Western Arctic stock has ranged from 14 to 72, amounting to an estimated 0.1-0.5% of the population.[45]
Baffin Bay and Davis Strait
[edit]In March 2008, Canada's Department of Fisheries and Oceans stated the previous estimates in the eastern Arctic had undercounted, with a new estimate of 14,400 animals (range 4,800–43,000).[49] These larger numbers correspond to prewhaling estimates, indicating the population has fully recovered. However, if climate change substantially shrinks sea ice, these whales could be threatened by increased shipping traffic.[50]
The status of other populations is less well known. About 1,200 were off West Greenland in 2006, while the Svalbard population may only number in the tens. However, the numbers have been increasing in recent years.[51]
Hudson Bay and Foxe Basin
[edit]The Hudson Bay – Foxe Basin population is distinct from the Baffin Bay – Davis Strait group.[52] The original population size of this local group is unclear, but possibly about 500 to 600 whales annually summered in the northwestern part of the bay in the 1860s.[53] It is likely that the number of whales that actually inhabit Hudson Bay is much smaller than the total population size of this group,[54] but reports from local indigenous people indicate that this population is increasing over decades.[55] Larger portions of the bay are used for summering, while wintering is on a smaller scale. Some animals winter in Hudson Strait, most notably north of Igloolik Island and north eastern Hudson Bay. Distribution patterns in these regions are affected by the presence of orca, and bowheads can disappear from normal ranges in the presence of atypical numbers of orca. Increased mortality caused by orca attack is a possible outcome of climate change, as reduced ice coverage is expected to result in fewer areas that the bowheads can use for shelter from attack.[55] Whaling grounds in the 19th century stretched from Marble Island to Roes Welcome Sound and to Lyon Inlet and Fisher Strait, and whales still migrate through most of these areas.
Distribution within Hudson Bay is mostly restricted to the northwestern part[52] along with Wager Bay,[56] Repulse Bay,[57] Southampton Island (one of two main known summering areas),[57][58] Frozen Strait, northern Foxe Basin, and north of Igloolik in summer.[55] Satellite tracking[59] indicates that some portions of the group within the bay do not venture further south than Whale Cove[57] and areas south of Coats and Mansel Islands.[citation needed] Cow – calf pairs and juveniles up to 13.5 m (44 ft) in length make up the majority of summering aggregation in the northern Foxe Basin, while matured males and noncalving females may use the northwestern part of Hudson Bay.[55] Fewer whales also migrate to the west coast of Hudson Bay and Mansel and Ottawa Islands.[55] Bowhead ranges within Hudson Bay are usually considered not to cover southern parts,[54][60] but at least some whales migrate to locations further south such as Sanikiluaq[citation needed] and Churchill river mouth.[61][62][63]
Congregation within Foxe Basin occurs in a well-defined area of 3,700 km2 (1,100 sq nmi) north of Igloolik Island to Fury and Hecla Strait and Kapuiviit and Gifford Fiord, and into Gulf of Boothia and Prince Regent Inlet. Northward migrating along western Foxe Basin to eastern side of the basin also occurs in spring.[55]

Sea of Okhotsk
[edit]Not much is known about the endangered Sea of Okhotsk population. To learn more about the population, these mammals have been regularly observed near the Shantar Islands, very close to the shore, such as at Ongachan Bay.[65][66] Several companies provide whale-watching services, which are mostly land-based. According to Russian scientists, this total population likely does not exceed 400 animals.[64] Scientific research on this population was seldom done before 2009, when researchers studying belugas noticed concentrations of bowheads in the study area. Thus, bowheads in the Sea of Okhotsk were once called "forgotten whales" by researchers. The WWF welcomed the creation of a nature sanctuary in the region[67]
Possibly, vagrants from this population occasionally reach into Asian nations such as off Japan or the Korean Peninsula (although this record might be of a right whale[68]). The first documented report of the species in Japanese waters was of a strayed infant (7 m (23 ft)) caught in Osaka Bay on 23 June 1969,[69] and the first live sighting was of a 10 m (33 ft) juvenile around Shiretoko Peninsula (the southernmost of ice floe range in the Northern Hemisphere) on 21 to 23 June 2015.[70] Fossils have been excavated on Hokkaido,[71] but it is unclear whether the northern coasts of Japan were once included in seasonal or occasional migration ranges.
Genetic studies suggest Okhotsk population share common ancestry with whales in Bering-Chukchi-Beaufort Seas, and repeated mixings had occurred between whales in the two seas.[72]
Svalbard-Barents Sea
[edit]The most endangered but historically largest of all bowhead populations is the Svalbard/Spitsbergen population.[73] Occurring normally in Fram Strait,[74] Barents Sea and Severnaya Zemlya along Kara Sea[51] to Laptev Sea and East Siberian Sea regions, these whales were seen in entire coastal regions in European and Russian Arctic, even reaching to Icelandic and Scandinavian coasts and Jan Mayen in Greenland Sea, and west of Cape Farewell and western Greenland coasts.[75] Also, bowheads in this stock were possibly once abundant in areas adjacent to the White Sea region, where few or no animals currently migrate, such as the Kola and Kanin Peninsula. Today, the number of sightings elsewhere is very small,[76] but with increasing regularities[77] with whales having strong regional connections.[78] Whales have also started approaching townships and inhabited areas such as around Longyearbyen.[79] The waters around the marine mammal sanctuary[80] of Franz Josef Land is possibly functioning as the most important habitat for this population.[81][82]
It is unclear whether this population is a remnant of the historic Svalbard group, recolonized individuals from other stocks, or if a mixing of these two or more stocks has taken place. In 2015, discoveries of the refuge along eastern Greenland where whaling ships could not reach due to ice floes[83] and largest numbers of whales (80–100 individuals) ever sighted between Spitsbergen and Greenland[84] indicate that more whales than previously considered survived whaling periods, and flows from the other populations are possible.
Possible moulting area off Baffin Island
[edit]During expeditions by a tour operator 'Arctic Kingdom', a large group of bowheads seemingly involved in courtship activities was discovered in very shallow bays south of Qikiqtarjuaq in 2012.[85] Floating skins and rubbing behaviours at sea bottom indicated possible moulting had taken place. Moulting behaviours had never or seldom been documented for this species before. This area is an important habitat for whales that were observed to be relatively active and to interact with humans positively, or to rest on sea floors. These whales belong to Davis Strait stock.
Isabella Bay in Niginganiq National Wildlife Area is the first wildlife sanctuary in the world to be designed specially for bowhead whales. However, moultings have not been recorded in this area due to environmental factors.[86]
Predation
[edit]In 1978 the International Whaling Commission (IWC) introduced a hunting strike quota for the Bering-Chukchi-Beaufort Sea (BCB) bowhead.[87] The quota has remained at 67 strikes per year since 1998 and represents about 0.5 percent of BCB population.[87] The population of bowheads in West Greenland and Canada is estimated to be 6,000 and rising, and hunts in this are minimal (<0.001 percent).[87] Both stocks are rising, and the indigenous hunts seem to be self-sustaining.[87] Orca are also known predators.[88] There is no consensus on the number of deaths by orca.[87] Bowheads seek the ice and shallow waters' safety when threatened by orca.[25] The Inuit have a traditional word for this behavior to give historical context that this is not a new phenomenon.[87] Global warming is increasing the frequency that orca are observed in the far north. A once-rare event, orca are now seen more frequently.[87]
There are no reports of attacks on bowheads by sharks.[87]
Whaling
[edit]
The bowhead whale has been hunted for blubber, meat, oil, bones, and baleen. Like the right whale, it swims slowly, and floats after death, making it ideal for whaling.[89] Before commercial whaling, they were estimated to number 50,000.[90] Paleo-Eskimo sites indicate bowhead whales were eaten in sites from perhaps 4000 BC. Inuit people near the Pacific developed specific hunting tools, with the whales providing food and fuel.[91]
Commercial bowhead whaling began in the 16th century when the Basques killed them as they migrated south through the Strait of Belle Isle in the fall and early winter. In 1611, the first whaling expedition sailed to Spitsbergen. The whaling settlement Smeerenburg was founded on Spitsbergen in 1619. By midcentury, the population(s) there had practically been wiped out, forcing whalers to voyage into the "West Ice"—the pack ice off Greenland's east coast. By 1719, they had reached the Davis Strait, and by the first quarter of the 19th century, Baffin Bay.[92]

In the North Pacific, the first bowheads were taken off the eastern coast of Kamchatka by the Danish whaleship Neptun, Captain Thomas Sodring, in 1845.[20] In 1847, the first bowheads were caught in the Sea of Okhotsk, and the following year, Captain Thomas Welcome Roys, in the bark Superior, of Sag Harbor, caught the first bowheads in the Bering Strait region. By 1849, 50 ships were hunting bowheads in each area; in the Bering Strait, 500 whales were killed that year, and that number jumped to more than 2000 in 1850.[93] By 1852, 220 ships were cruising around the Bering Strait region, which killed over 2,600 whales. Between 1854 and 1857, the fleet shifted to the Sea of Okhotsk, where 100–160 ships cruised annually. During 1858–1860, the ships shifted back to the Bering Strait region, where the majority of the fleet cruised during the summer until the early 20th century.[94] An estimated 18,600 bowheads were killed in the Bering Strait region between 1848 and 1914, with 60% of the total being reached within the first two decades. An estimated 18,000 bowheads were killed in the Sea of Okhotsk during 1847–1867, 80% in the first decade.[95]
Bowheads were first taken along the pack ice in the northeastern Sea of Okhotsk, then in Tausk Bay and Northeast Gulf (Shelikhov Gulf). Soon, ships expanded to the west, catching them around Iony Island and then around the Shantar Islands. In the Western Arctic, they mainly caught them in the Anadyr Gulf, the Bering Strait, and around St. Lawrence Island. They later spread to the western Beaufort Sea (1854) and the Mackenzie River delta (1889).[94]

Commercial whaling, the principal cause of the population decline, is over. Bowhead whales are now hunted on a subsistence level by native peoples of North America.[96]
In 2024, the Inuit hunters of Aklavik, Northwest Territories were permitted to hunt and kill one bowhead whale to distribute the whale meat, an important part of Inuit cuisine, to Inuvialuit and Gwich'in communities in the region.[97]
Alaskan subsistence
[edit]Some Alaska Natives continue by tradition to hunt bowhead and beluga whales on a subsistence level, with low annual bowhead total quotas set by the International Whaling Commission in conjunction with individual village limits set by the Alaska Eskimo Whaling Commission.[98]
Bowhead hunting is limited to whaling crews who are:[citation needed]
This bowhead subsistence hunting occurs during the northward spring migrations based from the ice and from small boats during the returning fall migrations.[99]
Whale bone fences
[edit]In the 18th century on the Frisian Islands the practice was common to line properties with fences of whale bones, not as status symbols or trophy displays, but just using the available resources on the treeless islands. The bones were mostly taken from the mandibles of bowhead whales. Two of these fences are still in place on the island of Borkum,[100] one on Rømø,[101] and small remains on Föhr, Ameland and Schiermonnikoog. The remaining fences are in a very weathered condition, while efforts are taken to preserve them for future generations.
Conservation
[edit]The bowhead is listed in Appendix I by CITES. While the global population is thought to be secure, thus assigned "least concern" status,[3] some populations are listed by the National Marine Fisheries Service as "endangered" under the auspices of the United States' Endangered Species Act. The IUCN Red List data are:[89]
- Svalbard population – critically endangered
- Sea of Okhotsk subpopulation – endangered
- Baffin Bay-Davis Strait stock – endangered
- Hudson Bay-Foxe Basin stock – vulnerable (estimated to be 1,026 individuals in 2005 by DFO)[102]
- Bering-Chukchi-Beaufort stock – lower risk – conservation dependent
The Alaska Department of Fish and Game and the USA government list the bowhead whale as federally endangered.[103]
The bowhead whale is listed in Appendix I[104] of the Convention on the Conservation of Migratory Species of Wild Animals (CMS), as this species has been categorized as being in danger of extinction throughout all or a significant proportion of its range. CMS Parties strive towards strictly protecting these animals, conserving or restoring the places where they live, mitigating obstacles to migration, and controlling other factors that might endanger them.[89]
Gallery
[edit]-
Whales swimming in the Lindholm Strait of the Shantar Islands, in the northwestern Sea of Okhotsk[105]
-
Cavorting whale in northwestern part of Sea of Okhotsk[64]
-
Blowholes
-
Resting in Foxe Basin
-
Fluke up before diving
-
Whale showing one of pectoral fins
-
Tip of whitish chin visible
-
Bowhead whale ranges – map centered over the North Pole
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ Mead, J. G.; Brownell, R. L. Jr. (2005). "Order Cetacea". In Wilson, D. E.; Reeder, D. M. (eds.). Mammal Species of the World: A Taxonomic and Geographic Reference (3rd ed.). Johns Hopkins University Press. pp. 723–743. ISBN 978-0-8018-8221-0. OCLC 62265494.
- ^ "Balaena mysticetus Linnaeus 1758 (bowhead whale)". Fossilworks.
- ^ a b c Cooke, J.G.; Reeves, R. (2018). "Balaena mysticetus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2018: e.T2467A50347659. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2018-1.RLTS.T2467A50347659.en. Retrieved 19 November 2021.
- ^ "Appendices | CITES". cites.org. Retrieved 14 January 2022.
- ^ Scammon, Charles M. (1874) The Marine Mammals of the North-Western Coast of North America, New York: G.P. Putnam's Sons, ISBN 1-59714-061-9.
- ^ Guinness World Records (14 November 2007). "Whale of a time!". Archived from the original on 17 November 2007. Retrieved 4 June 2009.
- ^ Fisheries, NOAA (27 June 2019). "Bowhead Whale | NOAA Fisheries". www.fisheries.noaa.gov. Retrieved 13 September 2019.
- ^ George, John C.; Bada, Jeffrey; Zeh, Judith; Scott, Laura; Brown, Stephen E.; O'Hara, Todd; Suydam, Robert (1999). "Age and growth estimates of bowhead whales (Balaena mysticetus) via aspartic acid racemization". Canadian Journal of Zoology. 77 (4): 571–580. doi:10.1139/cjz-77-4-571. ISSN 1480-3283.
- ^ Fisheries, NOAA. "Bowhead Whale (Balaena mysticetus): NOAA Fisheries". www.fisheries.noaa.gov. Archived from the original on 21 June 2017. Retrieved 18 September 2017.
- ^ Linnaeus, C (1758). Systema naturae per regna tria naturae, secundum classes, ordines, genera, species, cum characteribus, differentiis, synonymis, locis [System of nature through the three kingdoms of nature, according to the classes, orders, genera, species, with the characters, the differences, synonyms, places.] (in Latin). Vol. I (tenth, reformed ed.). Holmiae. (Laurentii Salvii). p. 824. Archived from the original on 19 March 2015.
- ^
Reilly, S.B.; Bannister, J.L.; Best, P.B.; Brown, M.; Brownell, R.L. Jr.; Butterworth, D.S.; et al. (2012). "Balaena mysticetus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2012: e.T2467A17879018. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2012.RLTS.T2467A17879018.en.
The taxonomy is not in doubt. ... Concerning common names, the species was once commonly known in the North Atlantic and adjacent Arctic as the Greenland Right Whale. However, the common name Bowhead Whale is now generally used for the species.
- ^ Rice, Dale W. (1998). Marine Mammals of the World: Systematics and distribution. Special Publication. Vol. 4. Society of Marine Mammalogy. ISBN 978-1-891276-03-3.
- ^ Kenney, Robert D. (2008). "Right Whales (Eubalaena glacialis, E. japonica, and E. australis)". In Perrin, William F.; Würsig, Bernd; Thewissen, J.G.M. (eds.). Encyclopedia of Marine Mammals. Academic Press. pp. 962–969. ISBN 978-0-12-373553-9.
- ^ Rosenbaum, H.C.; Brownell, R.L. Jr.; Brown, M.W.; Schaeff, C.; Portway, V.; White, B.N.; et al. (2000). "World-wide genetic differentiation of Eubalaena: Questioning the number of right whale species". Molecular Ecology. 9 (11): 1793–802. Bibcode:2000MolEc...9.1793R. doi:10.1046/j.1365-294x.2000.01066.x. PMID 11091315. S2CID 7166876.
- ^ "Whale bones found in highway were not from mystery whale". ScienceNordic.com. 7 February 2013.
- ^ a b c Würsig, B. and C. Clark (1993). "Behavior". In Burns et al.
- ^ a b Lowry, L. F. (1993). "Foods and Feeding Ecology". In Burns et al.
- ^ Haldiman, J. T. and R. J. Tarpley (1993). "Anatomy & Physiology". In Burns et al.
- ^ Scoresby, William (1820). An Account of the Arctic Regions with a History and a Description of the Northern Whale-Fishery. Edinburgh.
- ^ a b Bockstoce, J. R., and J. J. Burns (1993). "Commercial Whaling in the North Pacific Sector". In Burns et al.
- ^ a b c Koski, William R., Rolph A. Davis, Gary W. Miller, and David E. Withrow (1993). "Reproduction", p. 245 in Burns et al.
- ^ George, J.; Rugh, D.; Suydam, R. (2018). "Bowhead Whale: Balaena mysticetus". Encyclopedia of Marine Mammals (Third ed.). Princeton: Academic Press. pp. 133–135. doi:10.1016/B978-0-12-804327-1.00075-3. ISBN 9780128043271.
- ^ Eilperin, Juliet (18 October 2012). "Bowhead whales lost genetic diversity, study shows". The Washington Post.
- ^ Ford, T. J. Jr.; Werth, A. J.; George, J. C. (2013). "An intraoral thermoregulatory organ in the bowhead whale (Balaena mysticetus), the corpus cavernosum maxillaris". Anatomical Record. 296 (4): 701–708. doi:10.1002/ar.22681. PMID 23450839. S2CID 1181457.
- ^ a b c d Finley, K.J. (2001). "Natural History and Conservation of the Greenland Whale, or Bowhead, in the Northeast Atlantic" (PDF). Arctic. 54 (1): 55–76. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.500.2600. doi:10.14430/arctic764.
- ^ a b c Simmon, Malene; Johnson, Mark; Tyack, Peter; Madsen, Peter T. (2009). "Behaviour and Kinematics of Continuous Ram Filtration in Bowhead Whales (Balaena mysticetus)". Biological Sciences. 276 (1674): 3819–3828. doi:10.1098/rspb.2009.1135. PMC 2817290. PMID 19692400.
- ^ a b Bowhead Whale Archived 5 September 2015 at the Wayback Machine. American Cetacean Society. Retrieved on 16 November 2015.
- ^ "Balaena mysticetus (Bowhead)". Animal Diversity Web.
- ^ "Bowhead Whale : Baleen Whales : Voices in the Sea". Archived from the original on 21 September 2013. Retrieved 3 April 2013.
- ^ "SAFS Seminar: Kate Stafford, Scientific serendipity—unveiling the acoustic behavior of bowhead whales". University of Washington. Retrieved 14 January 2024.
- ^ Micu, Alexandru (5 April 2018). ""Bowhead [whales] are jazz," says researcher astonished by the diversity of their songs". ZME Science. Retrieved 5 April 2018.
- ^ George, John C.; Bada, Jeffrey; Zeh, Judith; Scott, Laura; Brown, Stephen E.; O'Hara, Todd; Suydam, Robert (1999). "Age and growth estimates of bowhead whales (Balaena mysticetus) via aspartic acid racemization". Canadian Journal of Zoology. 77 (4): 571–580. doi:10.1139/cjz-77-4-571. ISSN 1480-3283.
- ^ "A Whale of a Sliver". 15 June 2007.
- ^ "Can Marine Biology Help Us Live Forever? Bowhead Whale Can Live 200 Years, Is Cancer Resistant". Medical Daily. 6 January 2015. Retrieved 8 November 2015.
- ^ "'Lifespan clock' reveals bowhead whales live to 268...the oldest mammals on Earth". www.msn.com.
- ^ CSIRO. "Genetic 'clock' predicts lifespan in animals". www.csiro.au. Retrieved 19 April 2020.
- ^ a b "Researchers hope this whale's genes will help reverse human aging". The Washington Post. 6 January 2015. Retrieved 8 November 2015.
- ^ "Scientists map bowhead whale's genome; discover genes responsible for long life". Technie News. 5 January 2015. Archived from the original on 6 September 2018. Retrieved 5 January 2015.
- ^ "The bowhead whale lives over 200 years. Can its genes tell us why?". Science Daily. 5 January 2015. Retrieved 8 November 2015.
- ^ Moore, S. E., and R. R. Reeves (1993). "Distribution and Movement". In Burns et al.
- ^ Smultea, M.; Fertl, D.; Rugh, D. J.; Bacon, C. E. (2012). Summary of systematic bowhead surveys conducted in the U.S. Beaufort and Chukchi Seas, 1975–2009. U.S. Dep. Commer., NOAA Tech. Memo. NMFS-AFSC-237. p. 48.
- ^ Foote, A. D.; Kaschner, K.; Schultze, S. E.; Garilao, C.; Ho, S. Y. W.; Post, K.; Higham, T. F. G.; Stokowska, C.; Van Der Es, H.; Embling, C. B.; Gregersen, K.; Johansson, F.; Willerslev, E.; Gilbert, M. T. P. (2013). "Ancient DNA reveals that bowhead whale lineages survived Late Pleistocene climate change and habitat shifts". Nature Communications. 4: 1677. Bibcode:2013NatCo...4.1677F. doi:10.1038/ncomms2714. PMID 23575681.
- ^ "Bowhead Whales, and Not Right Whales, Were the Primary Target of 16th- to 17th-Century Basque Whalers in the Western North Atlantic" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 1 April 2010.
- ^ Field, Daniel J.; Boessenecker, Robert; Racicot, Rachel A.; Ásbjörnsdóttir, Lovísa; Jónasson, Kristján; Hsiang, Allison Y.; Behlke, Adam D.; Vinther, Jakob (1 March 2017). "The oldest marine vertebrate fossil from the volcanic island of Iceland: a partial right whale skull from the high latitude Pliocene Tjörnes Formation". Palaeontology. 60 (2): 141–148. Bibcode:2017Palgy..60..141F. doi:10.1111/pala.12275. hdl:1983/953db179-65ed-45e2-9c9e-e8d708ae7e75.
- ^ a b c "Bowhead Whale: Western Arctic Stock (December 30 2015)" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 15 May 2017. Retrieved 23 May 2017.
- ^ Givens, G; George, JC; Suydam, R; Tudor, B. (2021). "Bering-Chukchi-Beaufort Seas bowhead whale (Balaena mysticetus) abundance estimate from the 2019 ice-based survey". J. Cetacean Res. Manage. 22 (1): 61–73. doi:10.47536/jcrm.v22i1.230. S2CID 239498895.
- ^ Szesciorka, Angela R.; Stafford, Kathleen M. (7 February 2023). "Sea ice directs changes in bowhead whale phenology through the Bering Strait". Movement Ecology. 11 (8): 8. Bibcode:2023MvEco..11....8S. doi:10.1186/s40462-023-00374-5. PMC 9903510. PMID 36750903.
- ^ "Bowhead Quota". Alaska Eskimo Whaling Commission.
- ^ Eastern Arctic bowhead whales not threatened. Cbc.ca (16 April 2008). Retrieved on 15 September 2011.
- ^ Laidre, Kristin (22 January 2009) "Foraging Ecology of Bowhead Whales in West Greenland." Monster Jam. Northwest Fisheries Science Center, Seattle.
- ^ a b Norwegian Polar Institute. Bowhead whale (Balaena mysticetus). npolar.no
- ^ a b Higdon, J. W.; Ferguson, S. H. (2010). "Past, Present, and Future for Bowhead Whales (Balaena mysticetus) in Northwest Hudson Bay". A Little Less Arctic. pp. 159–177. doi:10.1007/978-90-481-9121-5_8. ISBN 978-90-481-9120-8.
- ^ Species Profile (Bowhead Whale) – Species at Risk Public Registry Archived 20 March 2016 at the Wayback Machine. Registrelep-sararegistry.gc.ca. Retrieved on 5 November 2016.
- ^ a b Hudson Bay-Foxe Basin bowhead whales, Stock status report E5–52. DFO Science, Canada
- ^ a b c d e f COSEWIC Assessment and Update Status Report on the Bowhead Whale Balaena mysticetus (PDF). COSEWIC. 2005. ISBN 978-0-662-40573-3.
- ^ Cosens, Susan E.; Innes, Stuart (2003). "Historical Population Characteristics of Bowhead Whales (Balaena mysticetus) in Hudson Bay". Arctic. 56 (3). doi:10.14430/arctic624. S2CID 131030979.
- ^ a b c Cosens, Susan E.; Innes, Stuart (March 2000). "Distribution and Numbers of Bowhead Whales (Balaena mysticetis) In Northwest Hudson Bay in 1995". Arctic. 53 (1): 36–41. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.172.4. doi:10.14430/arctic832. Retrieved 5 April 2018.
- ^ "Coral Harbour – Land and Wildlife". www.coralharbour.ca. Archived from the original on 18 April 2018. Retrieved 9 June 2017.
- ^ WWF. "June 2014: Bowheads and breaking ice – Thin Ice Blog".
- ^ "MPO – Recherche sur les mammifères marins au Canada – MPO Sciences". Archived from the original on 20 January 2016.
- ^ Reeves, Randall; Mitchell, Edward; Mansfield, Arthur; McLaughlin, Michele (1983). "Distribution and Migration of the Bowhead Whale, Balaena mysticetus, in the Eastern North American Arctic". Arctic. 36. doi:10.14430/arctic2243.
- ^ "Bowhead Whale in Churchill Waters – Churchill Polar Bears".
- ^ "Churchill Northern Studies Centre". Churchill Northern Studies Centre. Archived from the original on 15 June 2017. Retrieved 9 June 2017.
- ^ a b c Shpak, Olga (19 February 2014). "Второе рождение гренландского кита" (in Russian). RIA Novosti. Retrieved 4 June 2014.
- ^ "Тур 'наблюдение за китами и плавание вдоль побережья Охотского моря и на Шантарските острова'" (in Russian). Arcticexpedition.ru. 15 August 2000. Archived from the original on 19 June 2013. Retrieved 19 October 2012.
- ^ "Фотография: Киты подходят совсем близко к берегу" (in Russian). Turizmvnn.ru. 16 April 2011. Retrieved 19 October 2012.
- ^ "WWF приветствует создание нацпарка в Хабаровском крае" (in Russian). RIA Novosti. 31 December 2013. Retrieved 4 June 2014.
- ^ Smith, Tim D.; Reeves, Randall R.; Josephson, Elizabeth A.; Lund, Judith N. (27 April 2012). "Spatial and Seasonal Distribution of American Whaling and Whales in the Age of Sail". PLOS ONE. 7 (4): e34905. Bibcode:2012PLoSO...734905S. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0034905. PMC 3338773. PMID 22558102.
- ^ "大阪府漁業協同組合連合会". osakagyoren.or.jp.
- ^ ホッキョククジラか、知床沖遊泳 国内観察は極めてまれ. Asahi Shimbun (23 June 2015)
- ^ "いしかり博物誌/第5回 - 北海道石狩市公式ホームページ". city.ishikari.hokkaido.jp.
- ^ MacLean, Stephen Ahgeak (1 January 2002). Occurrence, behavior and genetic diversity of bowhead whales in the Western Sea of Okhotsk, Russia (Thesis). Texas A&M University.
- ^ Gross A., 2010 Background Document for Bowhead whale Balaena mysticetus. The OSPAR Convention and Musée des Matériaux du Centre de Recherche sur les Monuments Historiques. ISBN 978-1-907390-35-7. retrieved on 24 May 2014
- ^ Kovacs M.K., Bowhead whale (Balaena mysticetus). Environmental Monitoring of Svalbard and Jan Mayen. retrieved on 27 May 2014
- ^ Gilg O.; Born W.E. (2004). "Recent sightings of the bowhead whale (Balaena mysticetus) in Northeast Greenland and the Greenland Sea". Polar Biology. 28 (10): 796–801. doi:10.1007/s00300-005-0001-9. S2CID 5284359.
- ^ Ritchie B. (June 2013) Arctic shorts – bowhead whale. Vimeo. Retrieved 2 June 2014
- ^ Sala E. (2013) Franz Josef Land Expedition: First Look at Post-Expedition Discoveries. Pristine Seas Expeditions. National Geographic. retrieved on 24 May 2014
- ^ WIIG Ø., Bachmann L., Janik M.V., Kovacs M.K., Lydersen C., 2007. Spitsbergen Bowhead Whales Revisited. Society for Marine Mammalogy. Retrieved 24 May 2014
- ^ Johannessen, R. (19 October 2011) Dette er en sensasjon!. The Aftenposten. retrieved on 27 May 2014
- ^ Nefedova T., Gavrilo M., Gorshkov S., 2013. Летом в Арктике стало меньше льда Archived 24 May 2014 at the Wayback Machine. Russian Geographical Society. retrieved on 24 May 2014
- ^ European Cetacean Society. Bowhead whales (Balaena mysticetus) sighting in the Franz Josef Land area. Archived 23 May 2014 at the Wayback Machine. retrieved on 24 May 2014
- ^ Scalini I. (19 February 2014) Всемирный день китов. Russian Arctic National Park. retrieved on 24 May 2014
- ^ Walker, Matt (21 July 2015). "Secret whale refuge discovered". BBC.
- ^ "Exceptional sighting of 80+ Bowhead Whales". oceanwide-expeditions.com.
- ^ Lennartz T. (29 April 2013) New Bowhead Whale Molting Location Found. Arctic Kingdom. retrieved on 9 June 2014
- ^ Polar Bears and Glaciers of Baffin Island Webinar on Vimeo. Arctic Kingdom. 2014. retrieved on 9 June 2014
- ^ a b c d e f g h George, J. C.; Thewissen, J. G. M. (2020). The Bowhead Whale Balaena mysticetus: Biology and Human Interactions. Elsevier Science. ISBN 9780128189696.
- ^ Philo, L. M., E. B. Shotts, and J. C. George (1993). "Morbidity and Mortality." In Burns et al.
- ^ a b c "Bowhead Whale (Balaena mysticetus)". National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Retrieved 23 November 2015.
- ^ Woodby, D. A. and D. B. Botkin (1993). "Stock Sizes Prior to Commercial Whaling". In Burns et al.
- ^ "Giants of the Deep: A Prehistory of Whaling". resilience. 14 July 2021. Retrieved 15 July 2023.
- ^ Ross, W. G. (1993). "Commercial Whaling in the North Atlantic Sector". In Burns et al.
- ^ Demuth, Bathsheba (2019). Floating Coast: An Environmental History of the Bering Strait. W. W. Norton & Company. p. 40. ISBN 9780393358322.
- ^ a b Bockstoce, John (1986). Whales, Ice, & Men: The History of Whaling in the Western Arctic. University of Washington Press. ISBN 978-0-295-97447-7.
- ^ Vaughan, R. (1984). "Historical survey of the European whaling industry". In Arctic Whaling: Proceedings of the International Symposium, pp. 121–145. University of Groningen.
- ^ "Bowhead Whale". WWF. Retrieved 1 December 2015.
- ^ CBC News: For the first time in nearly 30 years, Aklavik, N.W.T., hunters can harvest a bowhead whale
- ^ Alaska's Population of Bowhead Whales Rebounding, Alaska Department of Fish and Game, Riley Woodford, November 2003. Retrieved 21 November 2016.
- ^ In hunt for bowhead whale, Alaska Native village preserves its past, Al Jazeera, Julia O'Malley July 25, 2015. Retrieved 21 November 2016.
- ^ "Heimatverein Borkum rettet Walknochenzaun" (PDF). Borkumer Zeitung. Retrieved 29 June 2023.
- ^ "Römös Sehenswürdigkeiten | Zaun aus Walknochen". Retrieved 29 June 2023.
- ^ Bowhead Whale, Walrus and Polar Bears of Foxe Basin on Vimeo. Arctic Kingdom. 2011. retrieved on 9 June 2014
- ^ Bowhead Whale (Balaena mysticetus). Alaskan Department of Fish and Game
- ^ "Appendix I" of the Convention on the Conservation of Migratory Species of Wild Animals (CMS). As amended by the Conference of the Parties in 1985, 1988, 1991, 1994, 1997, 1999, 2002, 2005, and 2008. Effective: 5 March 2009.
- ^ Vladislav Raevskii. Retrieved 1 June 2014
Cited sources
[edit]- Burns, J. J.; Montague, J. J.; Cowles, C. J., eds. (1993). The Bowhead Whale. Special Publication No. 2. Lawrence, Kansas: The Society for Marine Mammalogy. ISBN 0-935868-62-3.
External links
[edit]- "Bowhead whale: 200 year old whales". BBC Ocean Giants. October 2013. Archived from the original on 14 January 2017. Retrieved 9 April 2013.
- "The Bowhead Whale". Voices in the Sea, University of California San Diego. October 2013. Archived from the original on 21 September 2013. Retrieved 3 April 2013.
- "Bowhead Whale (Balaena mysticetus)". Office of Protected Resources, NOAA Fisheries. October 2013.
- "Bowhead whale (Balaena mysticetus)". ARKive. October 2013. Archived from the original on 22 April 2006. Retrieved 29 March 2006.
- "Harpoon may prove whale was at least 115 years old". World History Blog. October 2013. Archived from the original on 3 December 2008. Retrieved 23 June 2007.
- "In Search of the Bowhead Whale". NFB.ca. October 2013. A documentary by Bill Mason from 1974 following an expedition that searches out and meets the bowhead and beluga.
- "Balaena mysticetus". The TerraMar Project. March 2016. Archived from the original on 5 October 2016. Retrieved 29 March 2016.


![Whales swimming in the Lindholm Strait of the Shantar Islands, in the northwestern Sea of Okhotsk[105]](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/e/e5/Bowhead_whales_swimming_in_Lingolm_strait_by_Vladislav_Raevskii.JPG/120px-Bowhead_whales_swimming_in_Lingolm_strait_by_Vladislav_Raevskii.JPG)
![Cavorting whale in northwestern part of Sea of Okhotsk[64]](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/a7/A_bowhead_whale_is_tail-slapping_in_the_coastal_waters_of_western_Sea_of_Okhotsk_by_Olga_Shpak%2C_Marine_Mammal_Council%2C_IEE_RAS.jpg/120px-A_bowhead_whale_is_tail-slapping_in_the_coastal_waters_of_western_Sea_of_Okhotsk_by_Olga_Shpak%2C_Marine_Mammal_Council%2C_IEE_RAS.jpg)





